Knowledge
What is the difference between forged and machined parts?
In the mechanical industry, the choice between forged and machined parts can significantly impact the performance and cost of products. Understanding the differences between these two manufacturing methods is crucial for engineers and manufacturers.
As the highest quality in the industry, Vigor always insists on providing customers with customized products or solutions and ensures that the manufacturing of the products is always under control through strict quality control procedures. Before the product is packaged and shipped, Vigor's professional quality control personnel will also conduct 100% product inspection in the first place to ensure that all products are fully up to the customer's standards. If you are interested in casting or forging or machining products produced by Vigor, please do not hesitate to contact us for professional products and the highest quality service. Welcome to contact Vigor for more detailed information, call us at 029 81127932 or email us at info@castings-forging.com & marketing@vigordrilling.com
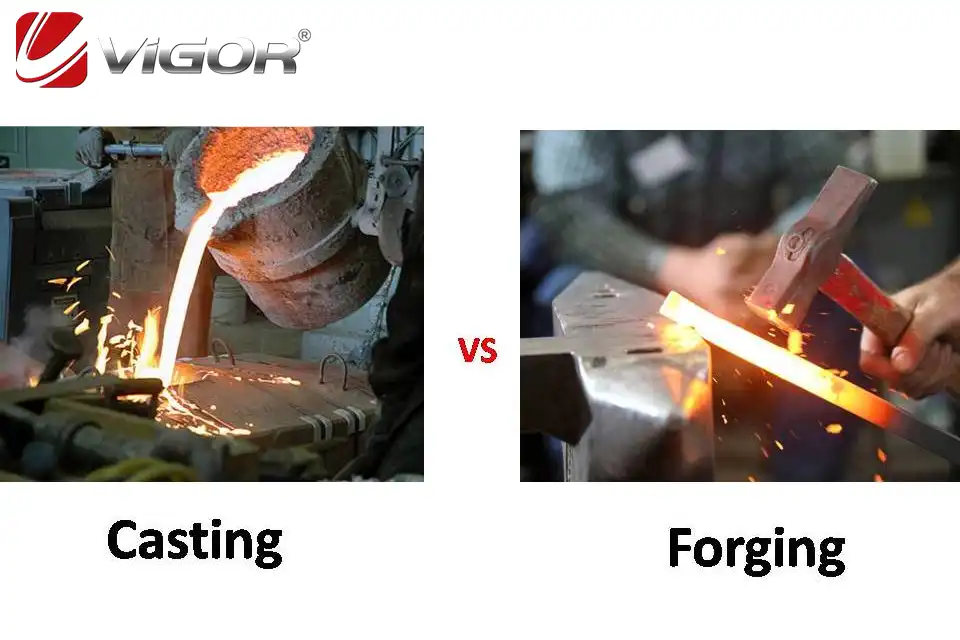
Forged parts are created through a process of shaping metal by applying compressive forces. This can be done using hammers, presses, or other forging equipment. The high-pressure deformation during forging refines the grain structure of the metal, resulting in improved mechanical properties. Forged parts typically exhibit higher strength, better fatigue resistance, and enhanced durability compared to other manufacturing methods. They are commonly used in applications where reliability and performance are critical, such as automotive engines, aerospace components, and heavy machinery.
On the other hand, machined parts are produced by removing material from a solid block of metal using cutting tools. This process allows for high precision and the creation of complex geometries. Machining can achieve tight tolerances and smooth surface finishes, making it suitable for parts that require close fits and precise dimensions. Machined parts are often used in applications where accuracy and functionality are key, such as in the production of medical devices, electronic components, and high-precision machinery.
One of the main differences between forged and machined parts lies in their material properties. Forging improves the metal's internal structure, aligning the grain flow along the part's shape. This alignment enhances the part's strength and resistance to stress. In contrast, machining does not alter the metal's grain structure to the same extent. While machined parts can still meet high-quality standards, they may not offer the same level of mechanical performance as forged parts in demanding applications.
Cost is another important factor to consider. Forging typically requires specialized equipment and tooling, which can make the initial investment relatively high. However, the high production rates and material utilization efficiency of forging can result in lower unit costs for large production volumes. Machining, on the other hand, is more flexible and can be used for small batch production or custom parts. The cost of machining depends on factors such as the complexity of the part, the machining time required, and the cost of the cutting tools.
In conclusion, the choice between forged and machined parts depends on the specific requirements of the application. Forged parts offer superior mechanical properties and are suitable for high-stress applications, while machined parts provide high precision and are ideal for complex geometries. By understanding the differences between these two manufacturing methods, engineers and manufacturers can make informed decisions that optimize product performance and cost.
In the mechanical industry, the choice between forged and machined parts can significantly impact the performance and cost of products. Understanding the differences between these two manufacturing methods is crucial for engineers and manufacturers.
As the highest quality in the industry, Vigor always insists on providing customers with customized products or solutions and ensures that the manufacturing of the products is always under control through strict quality control procedures. Before the product is packaged and shipped, Vigor's professional quality control personnel will also conduct 100% product inspection in the first place to ensure that all products are fully up to the customer's standards. If you are interested in casting or forging or machining products produced by Vigor, please do not hesitate to contact us for professional products and the highest quality service. Welcome to contact Vigor for more detailed information, call us at 029 81127932 or email us at info@castings-forging.com & marketing@vigordrilling.com
Forged parts are created through a process of shaping metal by applying compressive forces. This can be done using hammers, presses, or other forging equipment. The high-pressure deformation during forging refines the grain structure of the metal, resulting in improved mechanical properties. Forged parts typically exhibit higher strength, better fatigue resistance, and enhanced durability compared to other manufacturing methods. They are commonly used in applications where reliability and performance are critical, such as automotive engines, aerospace components, and heavy machinery.
On the other hand, machined parts are produced by removing material from a solid block of metal using cutting tools. This process allows for high precision and the creation of complex geometries. Machining can achieve tight tolerances and smooth surface finishes, making it suitable for parts that require close fits and precise dimensions. Machined parts are often used in applications where accuracy and functionality are key, such as in the production of medical devices, electronic components, and high-precision machinery.
One of the main differences between forged and machined parts lies in their material properties. Forging improves the metal's internal structure, aligning the grain flow along the part's shape. This alignment enhances the part's strength and resistance to stress. In contrast, machining does not alter the metal's grain structure to the same extent. While machined parts can still meet high-quality standards, they may not offer the same level of mechanical performance as forged parts in demanding applications.
Cost is another important factor to consider. Forging typically requires specialized equipment and tooling, which can make the initial investment relatively high. However, the high production rates and material utilization efficiency of forging can result in lower unit costs for large production volumes. Machining, on the other hand, is more flexible and can be used for small batch production or custom parts. The cost of machining depends on factors such as the complexity of the part, the machining time required, and the cost of the cutting tools.
In conclusion, the choice between forged and machined parts depends on the specific requirements of the application. Forged parts offer superior mechanical properties and are suitable for high-stress applications, while machined parts provide high precision and are ideal for complex geometries. By understanding the differences between these two manufacturing methods, engineers and manufacturers can make informed decisions that optimize product performance and cost.
Welcome to contact Vigor for more detailed information, call us at 029 81127932 or email us at info@castings-forging.com & marketing@vigordrilling.com